While the midterm elections will likely leave Congress in political gridlock, candidates from both major political parties supporting school choice policies won impressive victories. On the Republican side, with the exception of Arizona, every state in which the GOP held a trifecta—governor and both legislative chambers—going into the election and had “enacted large, new school-choice programs or significantly expanded existing ones in the past two years kept that trifecta,” noted The Heritage Foundation’s Jason Bedrick and Lindsey Burke.
The midterms helped illustrate school choice can be a winning policy issue for candidates. Voters in Florida’s Miami-Dade County, where about 75% of students are enrolled in school choice programs, issued a strong rebuke to Charlie Crist, a former Republican governor running as a Democrat, and his anti-school choice running mate Karla Hernandez-Mats, president of United Teachers of Dade. While President Joe Biden won Miami-Dade by seven points in 2020, Gov. Ron DeSantis trounced Crist with an 11-point victory in the county.
And this trend is not unique to school choice bastions like Florida. Corey DeAngelis pointed out in The Wall Street Journal that Democrats like Pennsylvania Gov.-elect Josh Shapiro, Gov. J. B. Pritzker of Illinois, and Gov. Kathy Hochul of New York won their races while supporting school choice policies.
Earlier this year, Pennsylvania Democrats in the state legislature, in particular, showed significant support for school choice when most “joined all legislative Republicans in enacting the largest expansion of the Keystone State’s school-choice policy in state history.”
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, support for school choice policies is strong. For instance, nearly 80% of Pennsylvania respondents, 76% of Illinois respondents, and 80% of New York respondents with school-aged children supported education savings accounts, according to an EdChoice poll.
Support for more flexible education options is unsurprising. Gallup polling from August 2022 showed that 55% of respondents were either somewhat or completely dissatisfied with the state of K-12 education, the highest level of dissatisfaction in the poll since 2018.
As the American Enterprise Institute’s Fredrick Hess noted, “Parents don’t really want to return to the status quo ante of public education. Indeed, more than half of all parents say—after the pandemic experience—that they’d like to retain some element of homeschooling going forward.”
In light of some sweeping school choice victories, policymakers and candidates on all sides of the aisle should embrace school choice policies that help students and appeal to parents and voters.
From the States
Reason Foundation’s new report, “Public schools without boundaries: A 50 state ranking of K-12 open enrollment,” shows that most states need to implement better student transfer policies.
Unfortunately, the study finds most states’ open enrollment options fall short of good policy. In fact, only 11 states require all school districts to participate in open enrollment, just three states require state education agencies to publish annual reports on student transfers, seven states require school districts to post their open seats by grade level, and only 24 states prohibit school districts from charging transfer students tuition. While no state meets every policy best practices on Reason Foundation’s open enrollment checklist, some states provide good models for other states to replicate.
Florida: The state’s open enrollment law could serve as a model for other states. All school districts in the Sunshine State are required to participate in both cross-district and within-district open enrollment and must regularly report the number of available seats by grade level so parents have access to this important information. Moreover, Florida cannot charge transfer students’ families tuition or fees, and the state’s school districts are allowed to provide transportation to transfer students, two barriers families in many other states face.
Wisconsin: The most laudable facet of Wisconsin’s open enrollment option is the state’s funding mechanism for transfer students, which ensures state and local education dollars follow transfer students. This approach maximizes transparency and financially incentivizes all districts to participate in open enrollment. Moreover, the Badger State is one of the few states to have robust, transparent open enrollment reporting. Every year Wisconsin publishes an open enrollment report which provides important data on student transfers, such as the number of transfer students, how many transfer applications were rejected, and the reasons for their rejection.
The study also highlights policies in each that are limiting students’ options and need to be reformed. For example:
Tennessee: Although Tennessee established a good within-district open enrollment policy in 2021, the state falls short in other important ways. For instance, cross-district open enrollment is voluntary in Tennessee, and all student transfers are at the discretion of the receiving local boards of education. Moreover, school boards can charge tuition or fees to transfer students. This can be a mammoth barrier for students whose families cannot afford the cost and creates perverse incentives for schools to “sell” their seats.
Ohio: Many wealthy and high-performing suburban school districts surrounding Ohio’s eight major cities refuse to participate in the state’s voluntary cross-district open enrollment program. This policy effectively keeps inner-city and nearby rural children from transferring to better schools in the suburbs. All too often, voluntary open enrollment means that the best schools with open seats can continue to exclude children from outside their boundaries, fundamentally undermining the program’s purpose.
Texas: In Texas, cross-district open enrollment occurs only upon the approval of the receiving school district. Similarly, voluntary within-district transfers are at the discretion of the school district, and parents must petition their school district, making a case for why their children should be transferred to another school. The school district then decides to accept or reject the transfer students’ petitions. To make matters worse, Texas allows school districts to charge transfer students tuition even though they receive additional state aid for transfer students.
What to watch
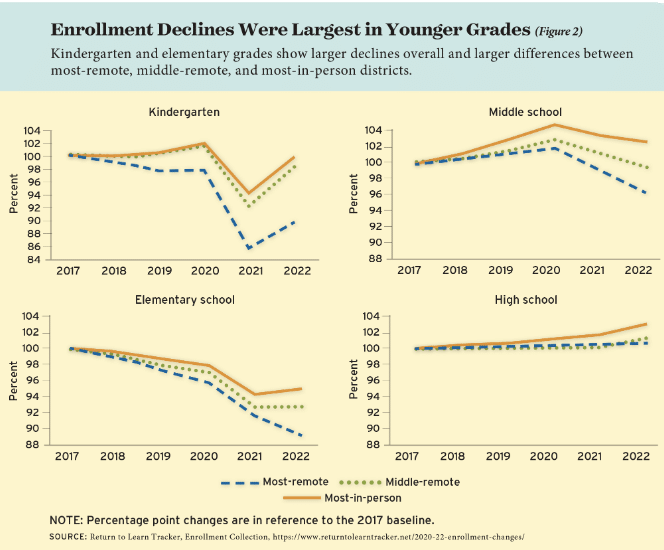
Report: Enrollment declines were larger in schools that stayed remote for the longest
A new Education Next report by Nat Malkus and Cody Christensen showed that schools that remained fully remote for longer periods suffered more significant drops in K-12 enrollment. In particular, the largest enrollment drops involved younger children in kindergarten and elementary school grades.
California voters support mandated K-12 arts funding as deficit looms
Over 60 percent of California voters approved Proposition 28, a ballot initiative that increases funding for K-12 music and arts education by approximately $1 billion. The Los Angeles Times reported that the new law establishes a “guaranteed annual funding stream for music and arts education by requiring the state to set aside an amount that equals 1% of the total funding already provided to schools each year.”
While music and arts can play important roles, the need will vary, and this new law illustrates how mandated state spending can encumber local education leaders’ decision-making and prevent them from putting resources where they are needed most. California policymakers recently approved increasing K-12 education funding by $9 billion for the 2023 school year–an increase of nearly 13% even though K-12 student enrollments dropped by 4.4% during the pandemic, so most schools should’ve already had the money needed for music and arts. As California’s state leaders predict a $24 billion deficit for the upcoming year, the new spending mandate could very well take funds away from other instructional programs educators would normally prioritize.
Recommended Reading
A Crypto Warning From the Ontario Teachers Pension Plan
Mike McShane at Forbes
“Making teacher benefits more portable and flexible would allow teachers to determine their own risk tolerance and invest accordingly. It would free up state funding for classrooms and the salaries of the people that work in them. And, it would help eliminate the incentives for these large pension funds to take on more and more risk, hopefully helping stabilize our financial system writ large.”
As New York City Schools Face a Crisis, Charter Schools Gain Students
Troy Closson at The New York Times
“As traditional public schools in the nation’s largest system endure a perilous period of student loss and funding shortfalls, New York City’s charter schools are on an upward trajectory. The schools gained more than 10,000 children during the pandemic, though the expansion slowed last year, even as enrollment at other schools across the city — both public and private — fell steadily.”
Beyond School Choice: A Conservative K-12 Agenda
Fredrick Hess at American Enterprise Institute
“Conservatives have generally lacked a cohesive K–12 agenda, but they can win parents over by enhancing educational choice, increasing school accountability, and adhering to standards of academic excellence.”

